
Probiotics are super popular these days, which may have you thinking, “Is this just another diet fad?” But no – probiotics and foods with probiotics are here to stay.
The truth is that cultures around the world have consumed foods with probiotics for centuries. In addition to buying the many probiotic products on the market today, you can easily make your own tasty and nutritious probiotic foods to boost your family's diet with surprisingly little effort or expense.
Though I'm a big fan of keeping life simple, the time involved to prepare these nourishing, healthful foods, is truly worth it. Your family's health and piggybank will benefit, and you may have fun in the process!
What are probiotics?
When you hear the word “probiotics,” you might think of acidophilus popularly found in yogurt, but yogurt is just one type of cultured and fermented food that is considered probiotic, and acidophilus is only one of the many strains of healthy microbes that can benefit your health.
Probiotics can be found in dairy, fruit or vegetable foods that are allowed to sour or ferment out of refrigeration deliberately. This ancient practice is called lacto-fermentation, and it not only makes food easier to digest, it also boosts their nutritional value and other health benefits. Yogurt and kefir, cultured vegetables, fermented beverages like kombucha are some of the probiotic foods eaten throughout the world today.
History of probiotics
The ancient Greeks, Middle Eastern, Asian and American Indian cultures all understood the advantage of fermenting foods, including food preservation, enhanced taste as well as health benefits.
- Miso, a fermented soybean, rice, barley or wheat paste, and pickled ginger have been featured in Japanese cuisine for centuries due to their ability to optimize digestion (especially of raw sushi).
- Fermented cabbage has long been a staple in the cuisine of cultures around the world, including Russia and Germany- where it is known as sauerkraut, and Korea's kimchi. It's renowned for its ability to aid digestion, especially diets rich in animal protein.
- Yogurt made with sheep's milk has been enjoyed in Greek cuisine for centuries, and Middle Eastern cultures have included fermented cheese in their diets for thousands of years.
- Native American cultures fermented a specially prepared corn (maize) dough for use as bread. Berries and other plant foods were fermented, and used in a process to prepare fermented corn (maize) dough as well.
At the start of the 20th century, scientists began to study the role microbes present in the intestinal tract played in health and the aging process. Fermented milk was identified as beneficial to health. Later, Russian scientist Elie Metchnikoff recommended the consumption of beneficial bacteria to help balance the ill effects of more harmful bacteria in human intestines. Eventually, the term probiotics was coined to contrast with “antibiotics,” which literally means “against life.”
Probiotic supplements have been popular in Europe for decades, and their popularity is slowly rising in the U.S. today.
Health benefits of foods with probiotics
Probiotics provide a wide variety of health benefits primarily by populating the digestive tract with healthy bacteria. During lacto-fermentation, healthy bacteria break the nutrients in food down into lactic acid.
Lactic acid is a natural preservative that stops the growth of harmful bacteria while at the same time promoting the growth of healthy micro-flora in the intestine. Other helpful enzymes and even anti-carcinogenic substances are also produced during lacto-fermentation.
Research has shown that probiotics ingested as a nutritional supplement are associated with:
- Optimizing digestion
- Enhancing the immune system
- Decreasing allergic reactions
- Reducing risk of some cancers
- Lowering blood pressure and cholesterol
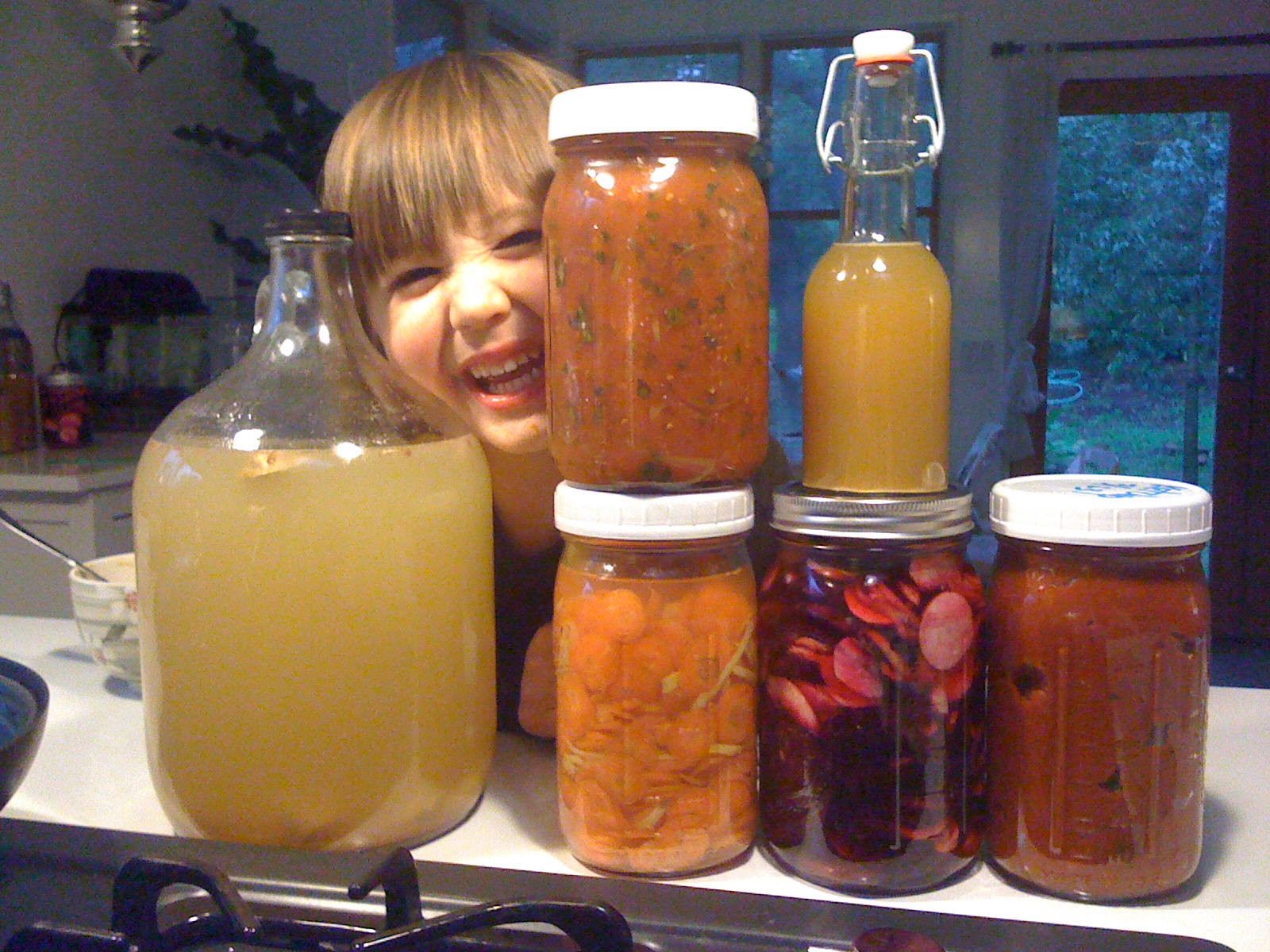
Four probiotic foods you can make at home
While you can easily buy probiotic supplements at health stores, making your own cultured foods is surprisingly easy, affordable, and fun. Kids love helping with these projects too!
 #1 – Kombucha
#1 – Kombucha
Kombucha is an effervescent, tangy beverage you can easily make yourself with very basic ingredients: black or green tea, sugar (1 gallon to 1 cup), and a kombucha culture, called a “SCOBY” – Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast. The ingredients are combined and fermented at room temperature for about 1 – 2 weeks.
Get you kombucha starter kit here.
The resulting beverage contains dozens of healthful elements including natural probiotics, B vitamins, acetic acid, amino acids, glucuronic acid, glucon acid, lactic acid, and more.
 #2 – Cultured veggies
#2 – Cultured veggies
Cultured vegetables are raw veggies that are allowed to ferment for about a week at room temperature so lactobacilli can grow, and then it is refrigerated until eaten.
Veggies such as cabbage, carrots, beets and garlic can be fermented into delicious “live” foods that maintain their lactobacillus-count for about 6 months after preparation. Veggies can be cultured with whey or sea salt, and taste like pickles or sauerkraut.
Some of the health benefits associated with cultured veggies include reducing symptoms of conditions such as colic (give baby a bit of the reserved veggie juice), peptic ulcers, food allergies, constipation and other digestive tract disorders.

#3 – Yogurt
Yogurt? Why not just buy it at the store? One of the most well known and most readily available probiotic foods, many varieties of store-bought yogurt are high in sugar and not very potent in probiotic content. Homemade yogurt is likely to contain more beneficial bacteria and less sugar, preservatives and chemicals – plus it's easy and fun to prepare.
All it takes to make yogurt at home is your choice of milk (preferably organic and raw), a starter yogurt culture for the first batch and some basic kitchen supplies. Your own homemade yogurt will be a great source of calcium, protein, magnesium and other essential vitamins as well as beneficial digestive tract bacteria without unnecessary additives.

#4 – Kefir
Kefir is a specially prepared, delicious fermented drink. There are 2 types of kefir- water and milk kefir, the latter can be made with sheep, goat or cow's milk. The liquid is fermented with kefir “grains”- (colonies of yeast and healthy bacteria), and the resulting drink is an excellent source of healthy intestinal micro flora, B vitamins, Vitamin E, and (for milk kefirs) complete proteins. Both water and milk kefir are also usually easily digested by those who are lactose-intolerant.
Making your own kefir requires nothing more than milk or water, kefir grains, and some basic kitchenware.
Once you become experienced at making your own probiotics at home, you'll find it's a great alternative to store-bought varieties. With a small investment of time and effort, you can enjoy the many benefits of probiotic foods you prepare and enjoy as part of your diet for long-term health.
Got a favorite probiotic food?
Let me know in the comments!










Great read thanks!!
How do I join the class to ferment food